Oral cavity cancer, also known as oral cancer or m...
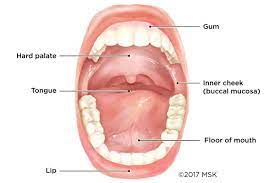
Oral cavity cancer, also known as oral cancer or mouth cancer, refers to cancer that develops in the tissues of the oral cavity, which includes the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, floor of the mouth, and the hard and soft palate. It's a type of head and neck cancer. Here are some key points to be aware of: 1. Causes and Risk Factors: • Tobacco use, including smoking and smokeless tobacco (chewing tobacco, snuff). • Excessive alcohol consumption. • Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, especially HPV16. • Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation. • A diet low in fruits and vegetables. • Exposure to certain chemicals and irritants. • Previous history of oral cancer. 2. Symptoms: • Persistent mouth sore or ulcer that doesn't heal. • Red or white patches on the lining of the mouth or tongue. • Pain, tenderness, or numbness in the mouth or lips. • Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking. • A lump or thickening in the mouth or neck. • Changes in voice. 3. Diagnosis: • Oral examination by a dentist or healthcare provider. • Biopsy: A sample of tissue is taken for analysis to confirm cancerous cells. 4. Staging: • Staging determines the extent of the cancer's spread. • It helps guide treatment decisions. • Stages range from 0 (pre-cancerous) to IV (advanced cancer). 5. Treatment: • Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. • Options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. • Surgery may involve removing the tumor, nearby lymph nodes, or parts of the oral cavity. 6. Prognosis: • Prognosis varies based on the stage and treatment effectiveness. • Early detection and treatment generally lead to better outcomes. 7. Prevention: • Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol consumption. • Maintain good oral hygiene. • Protect lips from sun exposure. • Get the HPV vaccine (if eligible).
Keywords
Subscribe for latest offers & updates
We hate spam too.


